HDR Video
Articles, guides, and resources about High Dynamic Range (HDR) video technology, including HDR10, Dolby Vision, color grading techniques, and HDR content processing.
Articles Tagged with "HDR"
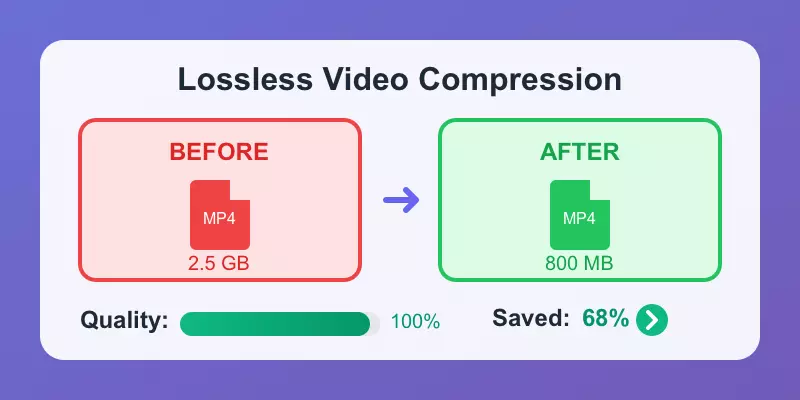
How to Compress Videos Without Losing Quality
Master professional video compression techniques while preserving HDR content quality. Learn about HDR-specific encoding settings and color space preservation.
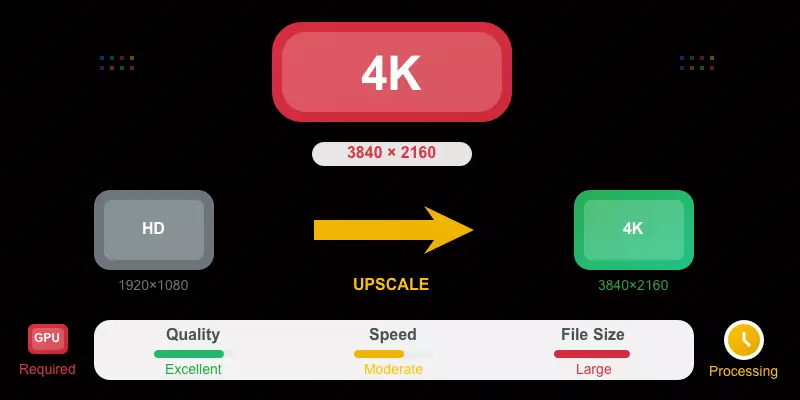
Read More4K Video Conversion: Best Practices and Settings
Master 4K video conversion with HDR support. Learn optimal settings for HDR10 and Dolby Vision content, hardware requirements, and quality preservation techniques.
Read MoreLearn More About HDR Video
About High Dynamic Range (HDR) Video
High Dynamic Range (HDR) video represents a revolutionary advancement in visual technology that dramatically expands the range of colors, brightness levels, and contrast ratios that can be displayed and captured. By supporting a wider color gamut, higher peak brightness, and deeper blacks, HDR creates more lifelike and immersive viewing experiences that closely match what the human eye naturally perceives. This technology has become essential for premium content across streaming platforms, gaming, and professional video production.
HDR Advantages
- Expanded color gamut: Billions more colors than standard video
- Higher brightness: Peak luminance up to 10,000 nits
- Deeper blacks: Enhanced contrast and shadow detail
- Natural appearance: More realistic lighting and colors
- Future-ready: Standard for next-generation displays
HDR Applications
- Streaming: Netflix, Amazon Prime, Disney+ HDR content
- Gaming: PlayStation 5, Xbox Series X HDR gaming
- Cinema: Dolby Vision theatrical releases
- Broadcasting: Live sports and events in HDR
- Mobile: HDR photography and video recording
HDR Standards & Formats
HDR10
Open standard: Royalty-free, widely supported
Static metadata: Fixed HDR parameters
10-bit color: 1.07 billion colors
Dolby Vision
Premium format: Dynamic metadata support
12-bit color: 68 billion colors
Scene-by-scene: Adaptive optimization
HLG
Broadcast standard: BBC/NHK developed
Backward compatible: Works with SDR displays
Live content: Optimized for broadcasting
HDR Technical Requirements
HDR Production Workflow
Creating HDR content requires careful attention throughout the entire production pipeline, from capture with HDR-capable cameras to color grading in HDR-aware environments, encoding with proper metadata, and delivery to HDR-compatible displays. Modern workflows often include tone mapping for SDR compatibility, ensuring content looks great on both HDR and standard displays while maximizing the visual impact for HDR-capable viewers.